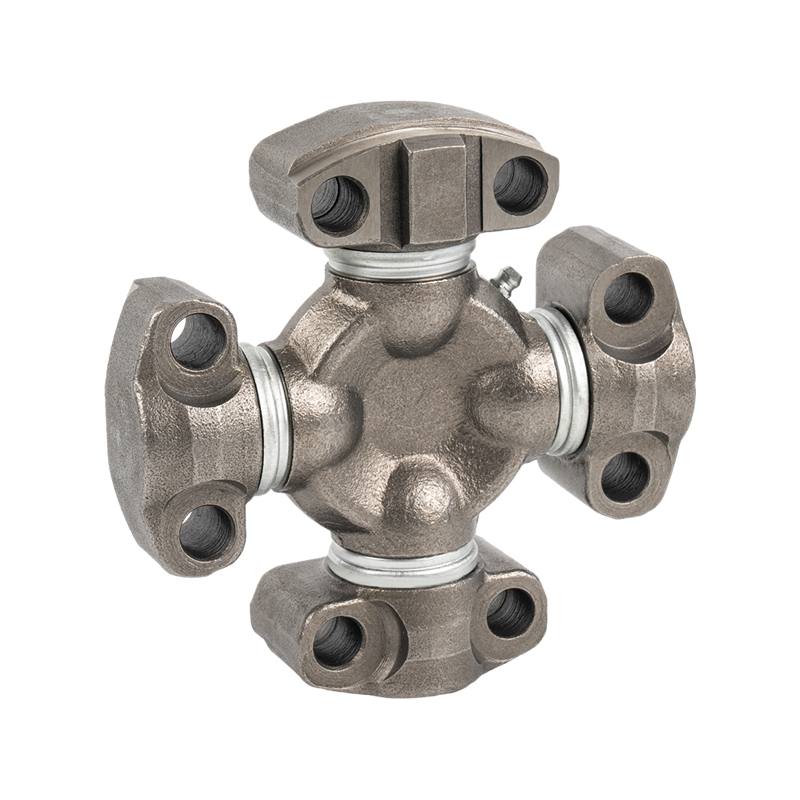
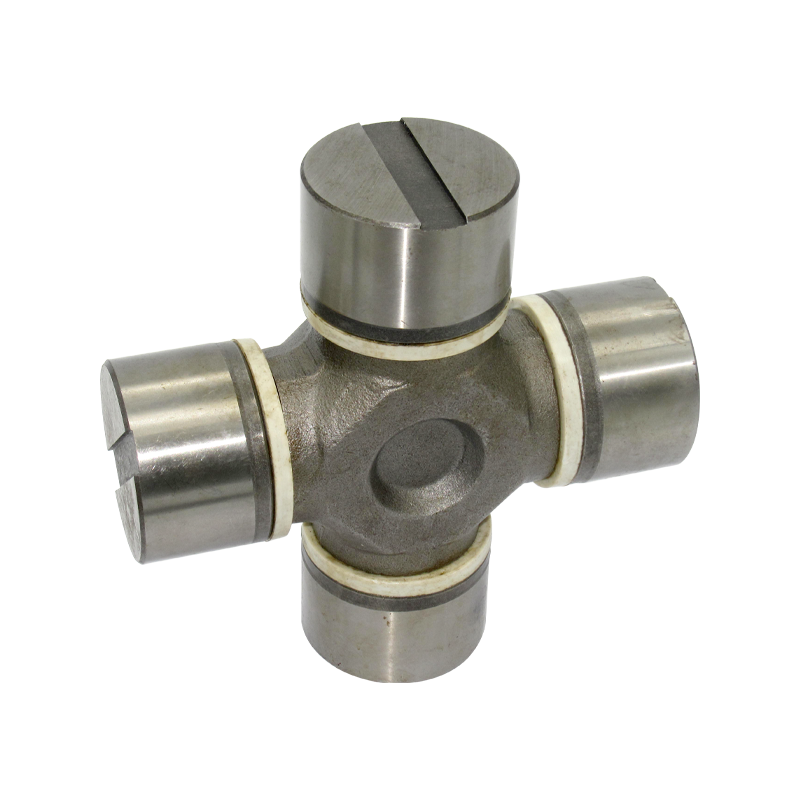
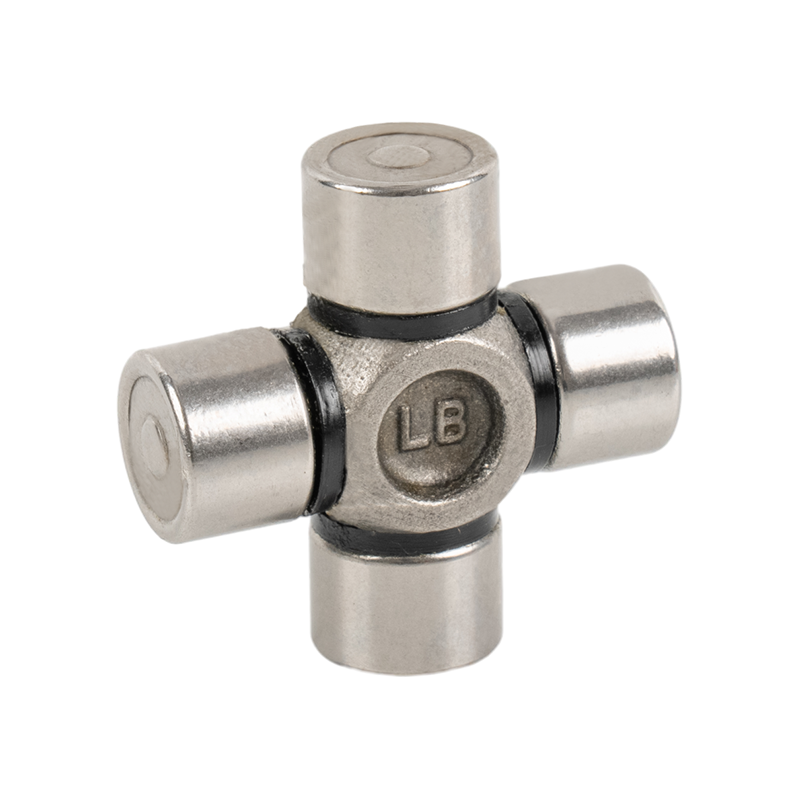
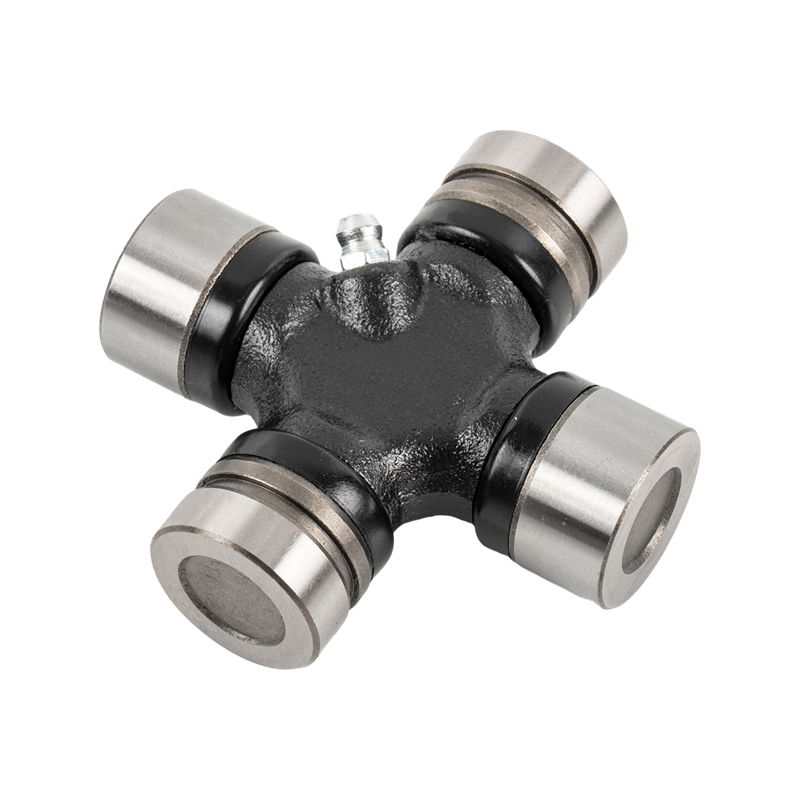
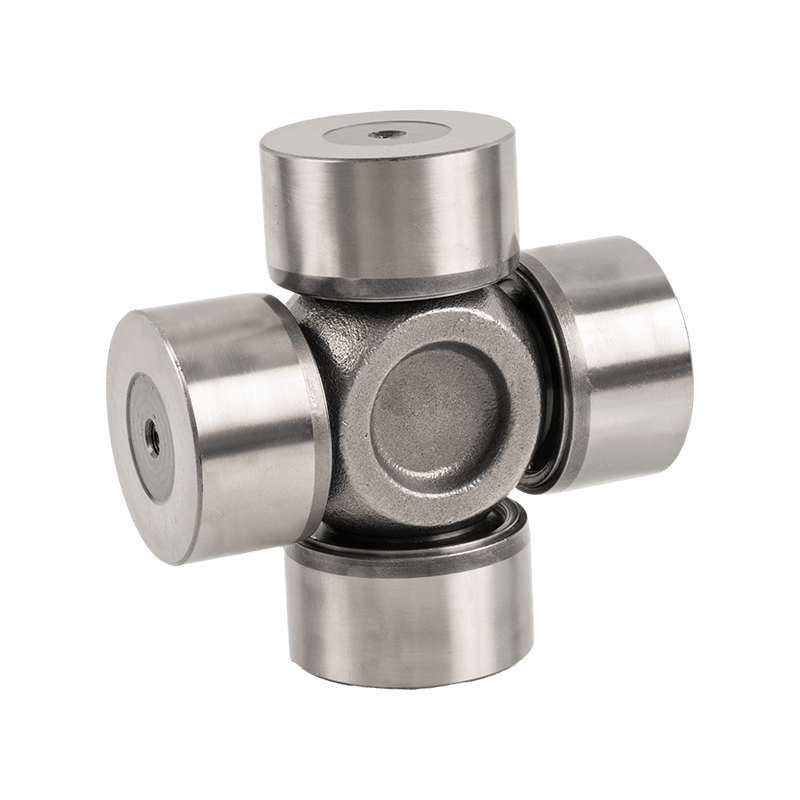
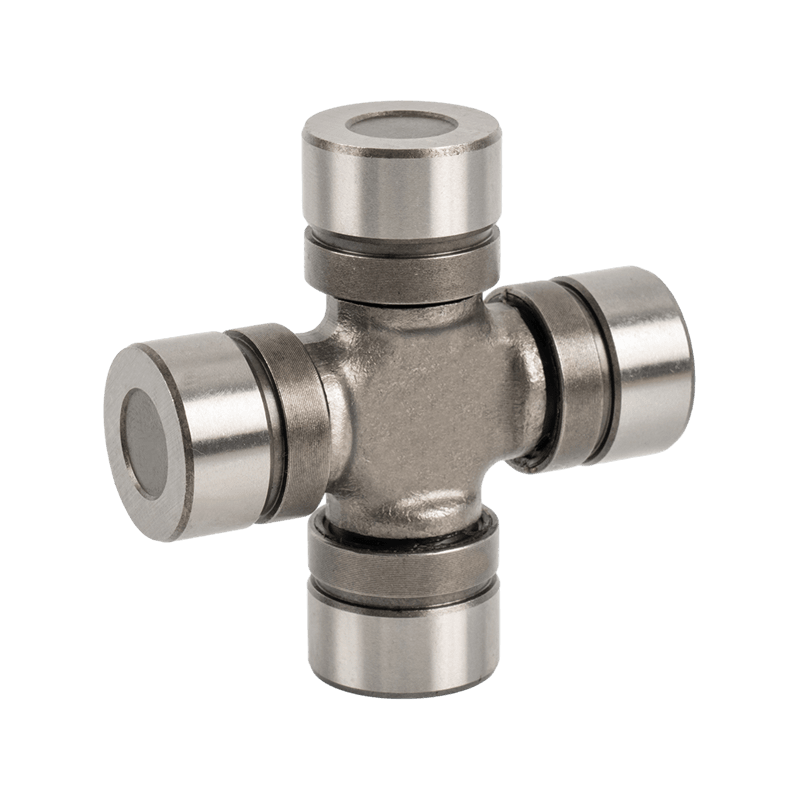
The core components of heavy-duty trucks are upgraded again, and Volvo Scania Benz Cross Joint enters the era of high strength
While the global commercial vehicle industry is constantly developing towards high efficiency, intelligence and high load, as a key component in the powertrain system, Volvo Scania Benz Cross Joint is ushering in technological innovation. Represented by world-leading heavy-duty truck manufacturers such as Volvo, Scania, and Benz, Cross Joint is experiencing an upgrade in the "high-strength era".
Coping with various working conditions, performance upgrade landing scene requirements
In the traditional commercial vehicle field, Cross Joint is often regarded as a basic component of "transmitting power", and its main function is to connect and transmit the power of the drive shaft. However, with the gradual increase in the load standards of heavy trucks, especially under high load, complex road conditions and long-term operation conditions, the working pressure of Cross Joint is far beyond imagination.
High load, high speed, high temperature difference, long-term operation, various climates and other working conditions require Cross Joint to have stronger adaptability and stability in performance. These challenges not only tested the durability, fatigue resistance and load-bearing capacity of the Cross Joint, but also put forward higher requirements for its manufacturing process.
In order to cope with these complex working conditions, engineers from brands such as Volvo, Scania, and Benz conducted in-depth technical research and development and successfully applied them to the power systems of the latest heavy-duty trucks.
Improved durability in high temperature, humid, and high-load environments
High temperature environments and frequent high-load operations often cause the loss or deterioration of lubricating grease inside the Cross Joint, resulting in increased wear and even component failure. Humid environments (such as coastal and humid mountainous areas) may cause the Cross Joint to rust and wear too quickly.
To this end, the three major brands introduced more high-temperature resistant alloy steel materials and used galvanizing or nitriding treatment on the surface of the Cross Joint to effectively prevent corrosion and wear in high temperature or humid environments. At the same time, new sealing technology is used to reduce the intrusion of moisture and sediment to ensure that the lubrication system is always in good working condition.
In addition, some high-end heavy-duty trucks have also added dynamic lubrication devices to the Cross Joint design to automatically adjust the amount of lubricating oil and provide additional lubrication protection when the vehicle is running under high load.
Vibration and impact response in mountainous and mining areas
Mountainous areas and mining areas are common working environments for heavy trucks, especially the high-frequency start-stop and strong vibration of mining transportation, which puts particularly stringent requirements on the Cross Joint. Under such working conditions, the Cross Joint must not only withstand large loads, but also cope with frequent impacts, vibrations and reverse stresses.
Traditional Cross Joints are usually difficult to cope with such strong reverse impacts, and are prone to "fatigue cracks" or "bearing shedding" problems. However, with the continuous advancement of technology, the current mainstream high-strength Cross Joint adopts an optimized cross-axis geometry design and reinforced steel materials to enhance its impact resistance. At the same time, the long-term impact of wheel vibration on the Cross Joint is reduced through the **dynamic balance design.
Under such complex high-load and vibration working conditions, the design of the Cross Joint requires not only impact resistance, but also stable torque transmission and low-friction operation, so as to maximize the working efficiency and safety of the vehicle power system.
Low temperature and ice and snow response in various climates
In addition to high temperature and humidity, the challenges of cold weather to the Cross Joint should not be underestimated. Low-temperature starting is a common problem for truck drivers in winter, especially in the cold Nordic region, where the temperature can drop to -40°C. In such an environment, the traditional Cross Joint is prone to brittle steel or even fracture due to low temperature.
In order to cope with the challenges in low-temperature environments, engineers from brands such as Volvo, Scania, and Benz have specially developed low-temperature crack-resistant alloy materials and optimized the lubrication system of the Cross Joint to ensure that the lubricant can flow effectively even in extremely cold conditions, maintaining the smoothness and durability of the Cross Joint.
In addition, some models are also equipped with electric heating devices to keep the lubricant of the Cross Joint flowing in extremely cold weather, avoiding early wear caused by poor lubrication.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体